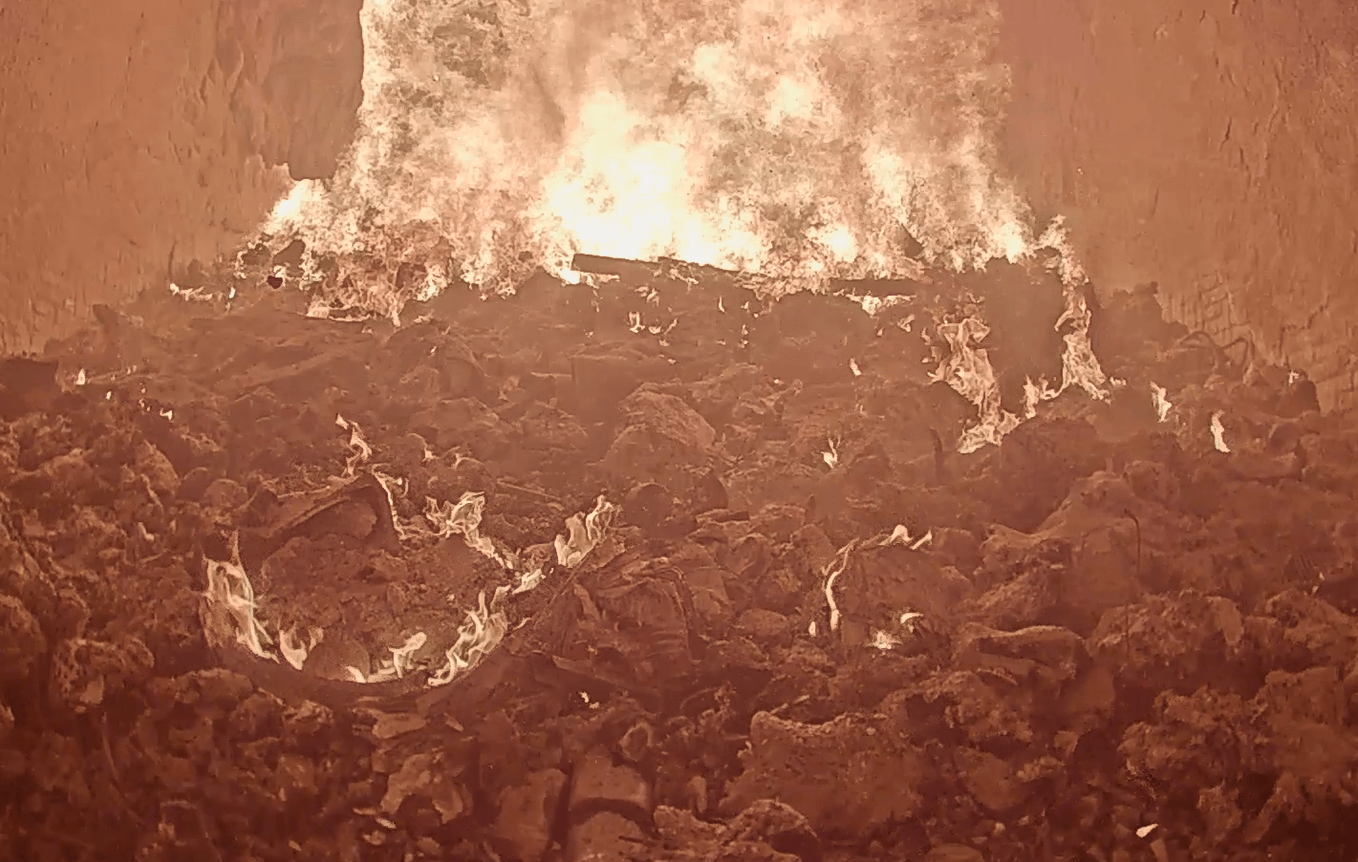Articles & News
Focus on the use of endoscopes in municipal waste incinerators
The basics of industrial inspection
Applications and use cases
Care and maintenance
Technologies and innovations
Modern incinerators play a crucial role in waste management, converting waste into energy while reducing its volume. However, these installations, which often operate 24/7, present major challenges in terms of maintenance, safety and efficiency. This is where industrial endoscopes come in, as they are essential tools for keeping incinerators running smoothly, while minimizing unplanned downtime.

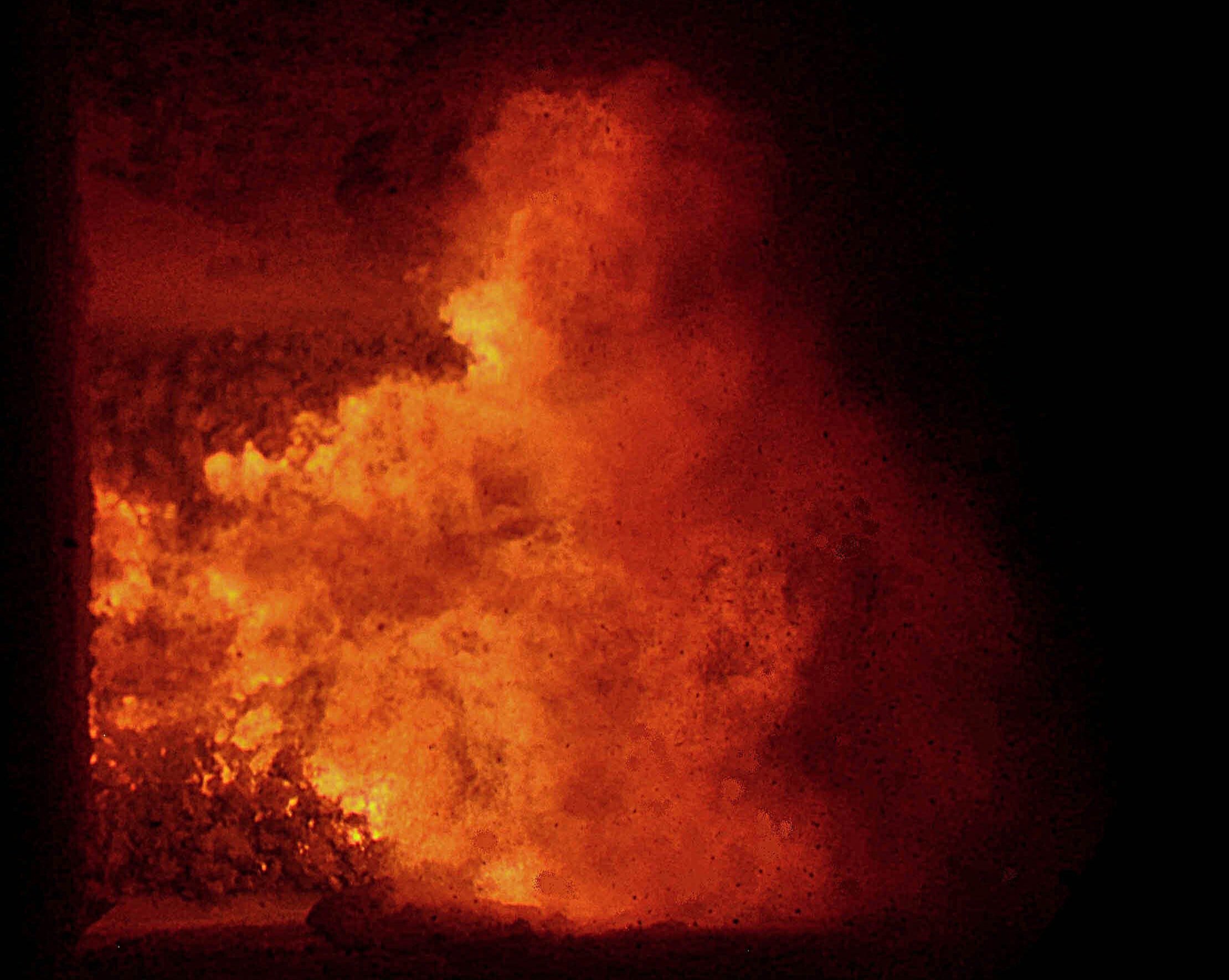
Explosions of nitrous oxide cylinders are a recurring problem at waste-to-energy plants. Up to 45 detonations a day can occur inside incinerators, generating thermal and mechanical shocks that weaken the infrastructure. These explosions cause cracks to form in refractory walls, burners to deteriorate and, in some cases, fires to break out.
This damage has a direct impact on plant operations. Prolonged shutdowns required for repairs impact on continuity of operations and site profitability. In France, these interruptions have accounted for losses of between 15 and 20 million euros over the past three years.
Troubleshooting :
By identifying anomalies early on, it reduces the risk of costly downtime.
Increased safety :
It limits operator exposure to hazardous environments.
Optimizing maintenance :
Predictive approach to planning repairs before the critical stage.
Operational efficiency :
Processes monitored in real time without interrupting production.
Key applications
Industrial endoscopes offer a high-performance solution for several key applications in incinerators:
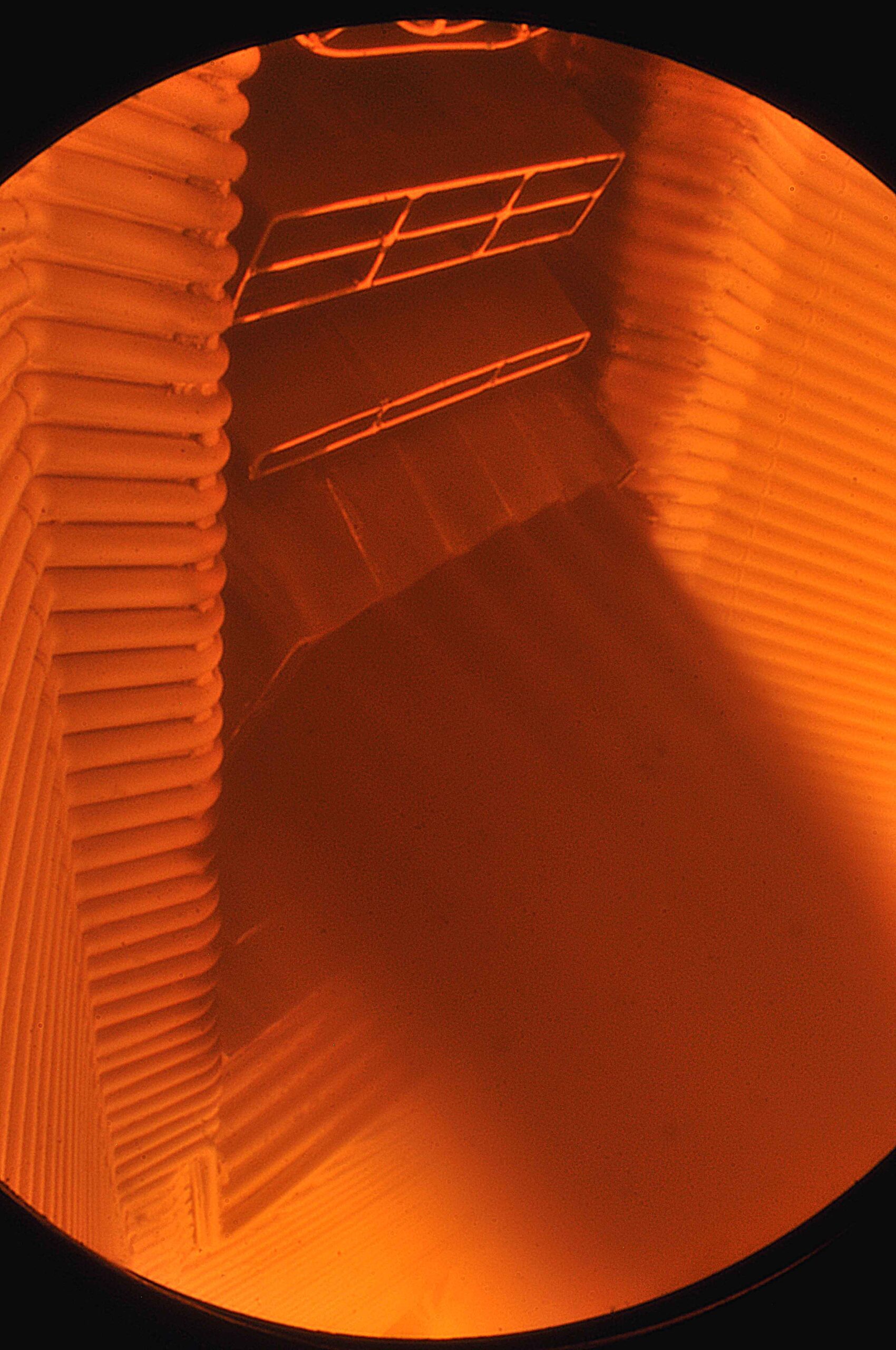
Furnace inspection: These inspections help optimize combustion by observing the way waste burns. This helps to adjust furnace parameters to maximize thermal efficiency.
Slag pits inspection: These pits, located at the bottom of incinerators, collect the solid residue from combustion (slag). Obstructions in these wells can lead to costly shutdowns. Endoscopes can be used to check their condition and quickly detect blockages.
Checking heat exchange systems: These systems play a key role in energy recovery. Endoscopes help identify dust deposits or obstructions that could reduce their efficiency.
Why use endoscopes?
There are many advantages to using industrial endoscopes in municipal waste incinerators:
High-resolution images: Thanks to advanced optical technologies, endoscopes provide detailed images that enable precise diagnosis of anomalies, such as cracks or deposits.
Remote intervention: Inspections can be carried out without operators having to enter hazardous areas directly, ensuring their safety.
Adaptation to extreme environments: Incinerators are hot, dusty and sometimes corrosive environments. Industrial endoscopes, with their built-in cooling systems and rugged design, are designed to operate in these harsh conditions.
Les bénéfices des inspections régulières
Les inspections régulières à l’aide d’endoscopes réduisent les risques d’arrêts imprévus, qui peuvent avoir un impact financier considérable sur l’exploitation. Elles permettent de :
- Prolonger la durée de vie des équipements en détectant les problèmes avant qu’ils ne deviennent critiques.
- Augmenter l’efficacité thermique de l’installation en assurant un fonctionnement optimal.
- Réduire les coûts de maintenance en permettant des réparations ciblées et planifiées.
Sectors dependent on industrial endoscopy :
Glass Industry
Inspection of glass furnaces to monitor melting of raw materials and detect refractory wear.
Steel and metallurgy
Control of burners and slab furnaces to ensure consistent production.
Energy
Boiler and incinerator diagnostics to identify blockages and maintain thermal efficiency.
Pour conclure :
Municipal waste incinerators represent an essential solution to today’s environmental and energy challenges. Industrial endoscopes are essential tools for guaranteeing their performance and safety. By providing accurate diagnostics and adapting to extreme conditions, they help keep these critical facilities running at peak performance, while reducing the risk of downtime and the associated costs.